It has been observed that food quality has a great impact on the morale of astronauts in space. Space food has evolved a lot since Yuri Gagarin dined on a meat paste from toothpaste-type tubes on mankind’s first space flight in 1961.
Now astronauts have a huge variety of good that they can consume in space. However, much of the food is still eaten straight from their packets. Dehydrated coffee, tea, milk and juices are rehydrated using a valve attached to the station in the ISS Service Module.
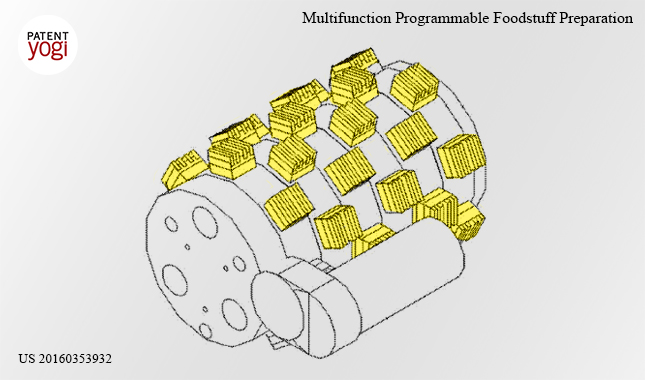
Currently, food ingredient dispensers and preparation devices typically have separate chambers for mixing ingredients and heating ingredients. More specifically, ingredients are mixed in a first vessel and subsequently transferred to an oven to create the final food product. The two containers occupy huge space. Moreover, conventional ingredient dispensers and mixers typically cannot operate in low or zero-gravity environments (e.g., the International Space Station (ISS)). Further still, conventional ingredient dispensers and mixers often require user intervention, and are not substantially automated.

Boeing has invented an automated food preparation device that prepares food for astronauts in space. The device uses a single container to mix and heat the food in the container.
An astronaut will be able to select a recipe from a recipe list provided by the patented food preparation device. In response to receiving the selection, the ingredients and preparation operations are retrieved from a memory device that is included in the food preparation device. The ingredients are automatically introduced into a container of the food preparation device. Then, based on the identified food preparation operations food ingredients are mixed and thermally regulated.
Further, the patented food preparation device uses thermoelectric devices to heat and cool the food. More specifically, heating and cooling operations associated with the food preparation device may also be used to heat and cool other components and systems such as environmental systems, payload areas, cryogenic systems, air exchangers, avionics fans, and air handlers. In this way, the heating and cooling of the food preparation device will be implemented to efficiently and effectively heat and cool other vehicle or space station components as well, thus increasing the overall efficiency of energy usage within the vehicle or space station.
Source: SpaceAnswers; Wikipedia
Publication number: US 20160353932
Patent Title: Multifunction Programmable Foodstuff Preparation
Publication date: 8 Dec 2016
Filing date: 16 Aug 2016
Inventors: George Wilson Freas, II;
Original Assignee: The Boeing Company
US20160353932