Biometric authentication techniques are becoming increasingly popular as alternatives to password-based techniques. Biometric authentication techniques are also being used as a part of multi-factor user authentication in addition to traditional passwords.
Not only do these techniques provide additional security to traditional passwords, but an additional advantage is also that users are no longer required to memorize complex text-based passwords. With increasing complexity requirements of text-based passwords, the biometrics are being accepted as a valid and more secure option providing a higher level of credibility for authenticating users.
One such technique is facial recognition and authentication. However, facial recognition is also susceptible to forgery, such as media-based facial forgery, and a malicious user can use a photo or video of a valid user to fool the authentication system. But no more.
Facebook has come up with an improved facial recognition and authentication system that is not prone to forgery.
Patented Technology
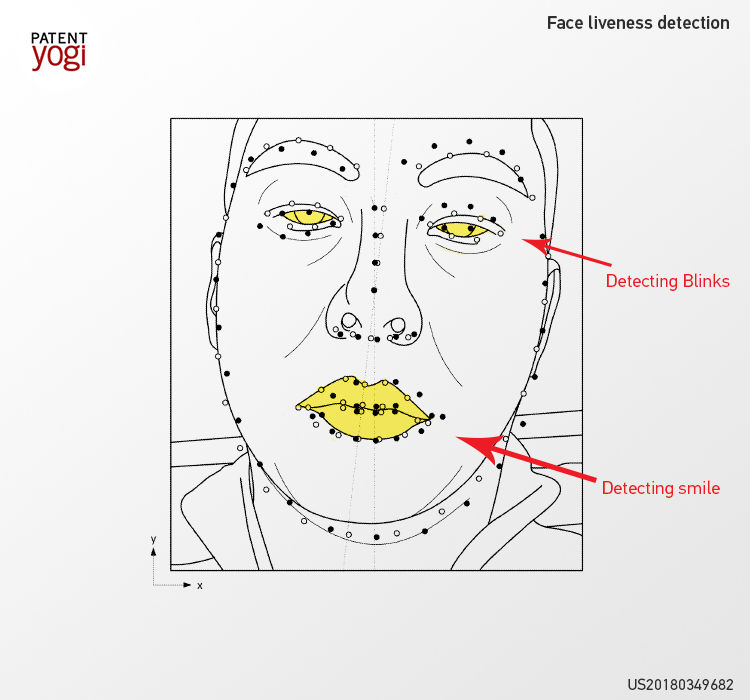
A recently published patent from Facebook talks about facial recognition and accurate liveness detection. Liveness detection detects whether a face captured by the camera of a device for facial unlocking is “live”, or an image or video of the face.
The system takes multiple image frames of the face. Then, the system analyzes the image frames and finds out if the user is blinking, smiling, or showing a movement of the head. Then, if a smile, blink, or head movement is detected, all these movements are compared against movements that are considered natural. For example, a person typically blinks more than 10 times in a space of a minute. If after comparison, all movements are determined to be natural, the face is accepted to be live.
Technical Details
The system receives a sequence of facial image frames. Then, additional information associated with the image frames like coordinates of feature points related to facial features, such as a position of eyes, lips, nose may determined from image frames. Then, the system determines liveness by detecting eye blinks in image frames. Eye blinks are determined based on a change in the opening area of the eye and finding closity values (including open, closing, and closed position). Then, based on a number of eye blinks, the face may be determined to be live.
Similarly, the system may detect a smile from the image frames. For example, a total height of the mouth, width-to-height ratio, opening height, area of the opening of the mouth, etc., will be calculated. Then, a change in these values will be compared with readings associated with authentic smiles.
Liveness detection will also detect head motions and determine the head motions to be authentic and natural to determine liveness.
Then, a combination of all these features will be used to determine liveness of a face.
Applications
Face recognition systems are using liveness detection techniques to prevent spoofing attacks. Unfortunately, such systems are also prone to spoofing attacks, like still-image based spoofing, video-based spoofing, and three-dimensional mask/model-based spoofing. Video-based spoofing and mask/model-based spoofing is difficult to perform as facial videos of most people are not readily available. It is also difficult to make 3D masks of faces as it requires special equipment (commonly seen in Mission Impossible movie series). Still-image based spoofing is relatively easy to perform as an imposter only has to rotate, shift, or bend a valid user’s photo in front of the camera to deceive the face recognition system.
Existing techniques also suffer from sensitivity to noise, low accuracy, low confidence level, additional hardware requirements, and user collaboration requirement. For example, blink detection, high-quality input data is needed.
Some techniques also need a pre-existing facial model for use as a reference or for pre-training. In such a scenario, Facebook’s technology may soon be implemented on all platforms and devices.
Publication Number: US20180349682A1
Patent Title: Face liveness detection
Publication date: 2018-12-06
Filing date: 2017-05-31
Inventors: Donald Kinhang Wong, Rajesh Janakiraman
Assignee: Facebook Inc