Speech recognition includes processes for converting spoken words to text or other data. In general speech recognition systems translate verbal utterances into a series of computer-readable sounds and compare those sounds to known words. For example, a microphone may accept an analog signal, which is converted into a digital form that is then divided into smaller segments. The digital segments can be compared to the smallest elements of a spoken language, called phonemes (or “phones”). Based on this comparison, and an analysis of the context in which those sounds were uttered, the system is able to recognize the speech.
To this end, a typical speech recognition system may include an acoustic model, a language model, and a dictionary. Briefly, an acoustic model includes digital representations of individual sounds that are combinable to produce a collection of words, phrases, etc. A language model assigns a probability that a sequence of words will occur together in a particular sentence or phrase. A dictionary transforms sound sequences into words that can be understood by the language model.
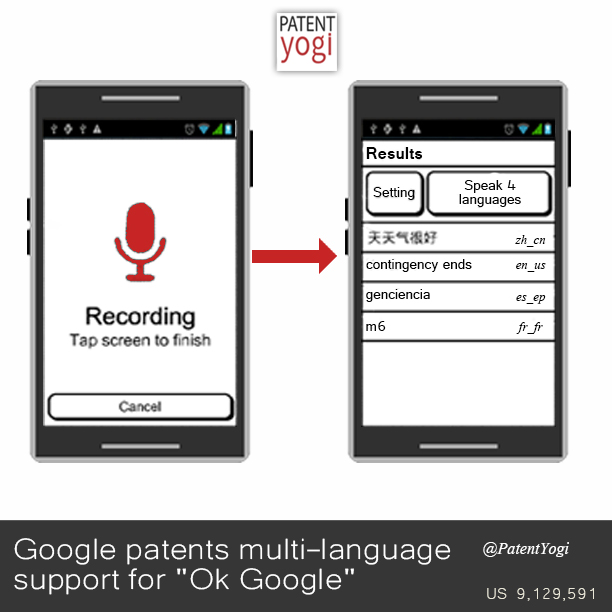
Described herein are speech recognition systems that may perform the following operations: receiving audio; recognizing the audio using language models for different languages to produce recognition candidates for the audio, where the recognition candidates are associated with corresponding recognition scores; identifying a candidate language for the audio; selecting a recognition candidate based on the recognition scores and the candidate language; and outputting data corresponding to the selected recognition candidate as a recognized version of the audio. The speech recognition systems may include one or more of the following features, either alone or in combination.
Identification of the candidate language may be performed substantially in parallel with recognition of the audio using the language models for different languages, or the identification may occur prior to recognition of the audio using the language models for different languages. Selecting the recognition candidate may include taking agreement of different language models into account when deciding which recognition candidate to select.
The above-described systems may include selecting the language models. The language models may be selected based on input from a user from whom the audio is received.
Selecting the language models may include: identifying languages associated with previously-received audio; and selecting language models corresponding to the identified languages.
Patent Information
Patent Number: US US 9,129,591
Patent Title: Recognizing speech in multiple languages
Inventors: Sung; Yun-hsuan (Mountain View, CA), Beaufays; Francoise (Mountain View, CA), Strope; Brian (Palo Alto, CA), Lin; Hui (Seattle, WA), Huang; Jui-Ting (Fremont, CA)
Assignee: Google Inc. (Mountain View, CA)
Family ID: 1000001325434
Appl. No.: 13/726,954
Filed: December 26, 2012
Abstract: Speech recognition systems may perform the following operations: receiving audio; recognizing the audio using language models for different languages to produce recognition candidates for the audio, where the recognition candidates are associated with corresponding recognition scores; identifying a candidate language for the audio; selecting a recognition candidate based on the recognition scores and the candidate language; and outputting data corresponding to the selected recognition candidate as a recognized version of the audio.
Want a patent for your invention, share details with us for a free patent search – https://patentyogi.com/novelty-search/.