Air conditioning (or controlled ambient temperature) is ubiquitous in all indoor settings such as meeting rooms, class rooms, auditoriums, and theaters across the world.
Air conditioners need a lot of energy during operation. A typical room air conditioner uses 10-20 times as much electricity as a ceiling fan. However, the costs of energy and attendant energy processing have been increasing due to rising energy demands resulting from worldwide industrialization and the depletion of the energy resources in the world. Yet, the demand for air conditioning is increasing every year. For example, in China, sales of air conditioners have nearly doubled over the last five years. Worldwide power consumption for air conditioning alone is forecast to surge 33-fold by 2100 as developing world incomes rise and urbanization advances.
Also, the disposal and recycling of the by-products of energy consumption have given rise to increasing costs and potential health problems with energy consumption waste products. Air conditioning is doubly polluting: they are powered by energy produced from fossil fuels, further, they use HFCs and other refrigerants cooling systems which cause global warming. Therefore, there is a need to reduce energy consumption using air conditioners.

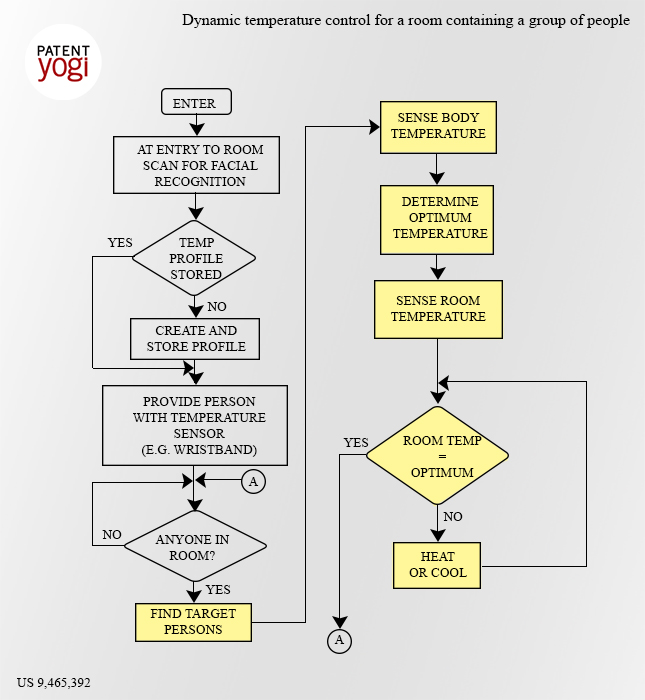
IBM plans to use the digital processing to bring down the costs and effects of energy consumption. Specifically, IBM has developed a system to achieve optimum temperatures in rooms containing people to minimize energy waste and maximize the temperature related comfort of the people in the room. The system directly and dynamically senses the body temperatures of one or more people in the room. The sensed body temperatures are wirelessly transmitted to be correlated a set of parameters. In response to this correlation, a selected optimum room temperature is provided by appropriate heating or cooling.
Further, the number or proportion of people in the room who are temperature sensed can be varied from only one person to all of the people in the room. The hosts of a function can determine whose body temperature should be monitored dependent upon the circumstances of the presentation in the room. Person may be selected based on their significance, for example, a minister delivering a sermon or a chief executive at a stockholders meeting. Further, the people may be chosen based on the extent of their activity, e.g. a set of performers in a theater may be chosen.
Moreover, wristbands may be give to people whose body temperature will be monitored. The wristband would include a minute temperature sensor and a short range RF transmitter.
Publication number: US 9,465,392
Patent Title: Dynamic temperature control for a room containing a group of people
Publication date: 11 Oct 2016
Filing date: 14 Nov 2012
Inventors: Lisa Marie Wood Bradley; Marissa Ann Wood; Nan Li; Charles Edmond Wiese;